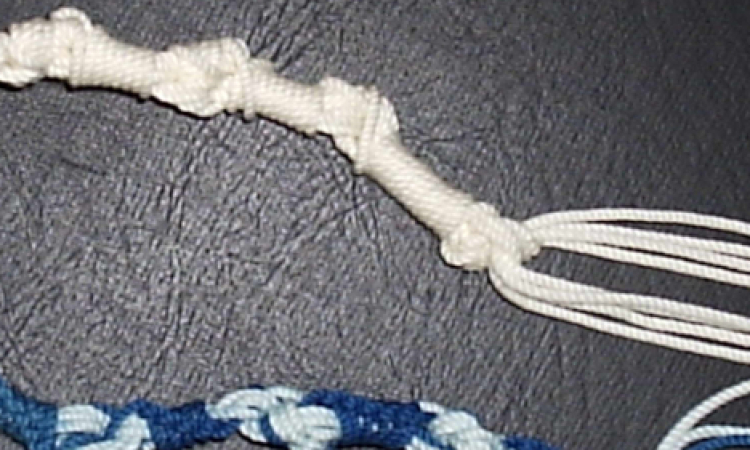
The custom of putting Tsitsit, fringes or tassels, on the corners of garments originates in the biblical commandment:
Speak to the people of Israel, and bid them that they make them fringes in the borders of their garments throughout their generations, and that they put upon the fringe of the borders a thread of blue; And it shall be to you for a fringe, that you may look upon it, and remember all the commandments of the Lord, and do them. Numbers 15, 38-9.
The custom is clearly old and was probably a form of tribal identification, which separated the Israelites out from gentiles. This is shown by the fact that a Jew was not allowed to sell a garment with fringes to a non-Jew without removing the fringes first.
By the time of the Mishnah in the early 3rd Century fringes were accepted as a long-standing practice. However, the Rabbis were still arguing just how many blue and how many white threads were required. The blue (T'chelet) was provided by the dye obtained by a sea snail called in Hebrew (Chilazon). But these became scarce and the Mishnah permitted the use of tsitsit with all white threads. Eventually a severe snail shortage caused people to stop and then forget the dyeing process. Today it is the custom to have undyed fringes. Only a minority want to introduce the use of blue threads, in case it is the wrong dye or the wrong colour, and so invalidate the fringe.
A further development occurred when Jews who moved into Europe adopted modern dress. Unlike the rectangular sheet of Eastern garments, western clothes did not always have corners. The Shulchan Aruch permitted the wearing of outer garments without fringes. Instead, Jews began wearing a Tallit for prayers and a (Tallit Katan) under their outer garments, and these had fringes in order comply with biblical command. In the 13th century the wearing of tsitsit was not a common practice.
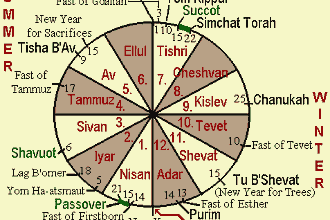
Originally found here
Picture originally found here